1. In the earliest phase of UK history, the English conquered their neighbors to the north: __. a) Scots b) Irish c) Welsh d) French.
2. The English also won conquest of their neighbors on a nearby island: __ . a) Scots b) Irish c) Welsh d) French.
3. The English defeated their immediate western neighbors, the __ people. a) Scots b) Irish c) Welsh d) French.
4. The British controlled one strategic territory in the Mediterranean: the island of __ .
5. In West Africa the English left a legacy in controlling the nation of __ .
6. The British won the diamonds and gold in South Africa. The capital of that nation is __ .
7. Several nations in East Africa - land of ivory and spices - were long managed by the British. Name one of them: __ .
8. In the Middle East the English controlled Jordan, Iraq and Palestine, today called __ .
9. India was a valuable land of gemstones, gold and spices. The British controlled much of India for over 200 years. The capital is Delhi. On the east is Kolkata. On the west is the city nicknamed Bollywood: __ .
10. Based on its dominance in India, would you guess that the English were also rulers of Afghanistan, Pakistan, Bangladesh and Burma? a) yes b) no.
11. The Dutch controlled Indonesia - oil and coffee - and the French controlled Vietnam - rubber and gemstones - while the British controlled the city at the end of the Malay Peninsula: __ .
12. Opium and pearls were part of the British profit from the island city on the South China Sea called __ __ .
13. One of the world's most active ports - near the mouth of the Yangtze River and on the East China Sea - was an important profit center of the British: a) Beijing b) Taipei c) Shanghai d) Hong Kong.
14. The British made Australia a colony - land, sheep and minerals were valuable - but a student can examine the names of New Zealand's cities and guess that the French were the colonizers of New Zealand. T / F
15. Vancouver was long a British possession. T / F
16. In the northern nation of __, the British profit center was fur and timber. a) Iceland b) Denmark c) Canada d) Russia.
17. In the Caribbean, the money lay in sugar and spices. Port of Spain is capital of the island of __.
18. Indigenous people the Taíno called this island "Xaymaca," which meant the "Land of Springs". The Spanish called it Santiago. The British called it __ .
19. This city was called New Amsterdam when it was colonized by the Dutch. When the British took possession it was renamed for the Duke of __ .
20. Based on the names found on the islands of the Bahamas and Bermuda, would you guess that both these islands or only one of them was colonized by the British? a) one b) both.
Thursday, November 29, 2012
British Empire quiz
Wednesday, November 28, 2012
The Thames, the Tower Bridge and the Tower of London / sketch Robert Trudeau
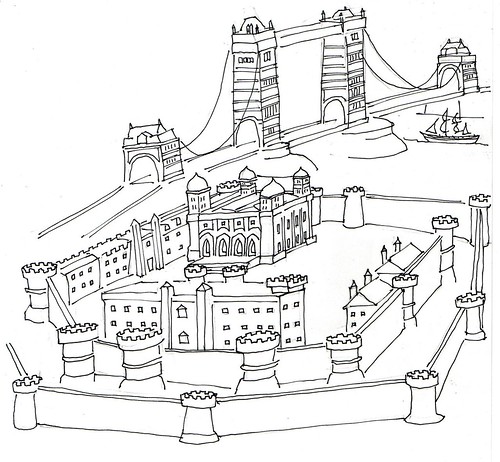
The Thames, the Tower Bridge and the Tower of London / sketch Robert Trudeau, a photo by trudeau on Flickr.
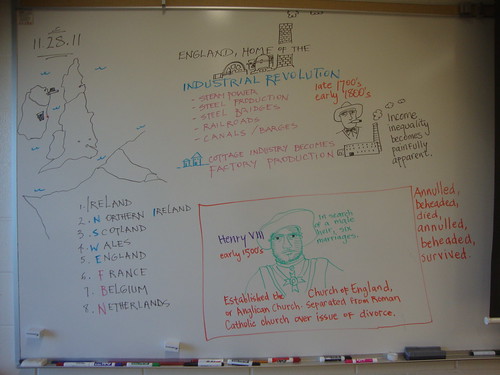
The British Isles map -
- England
- Wales
- Scotland
- Northern Ireland
- Ireland (Eire)
- France
- Belgium
- Netherlands
- Nord ee
- English Channel (La Manche)
- Atlantic
- London
- Stonehenge site
- Loch Ness
- Edinburgh (golf)
- Belfast (Titanic)
- Welsh / English castles
- Celts: the tribal peoples of Western Europe.
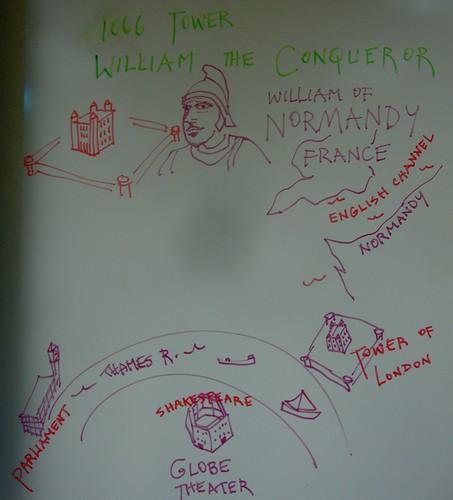
Tower of London - Her Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress, more
commonly known as the Tower of London, is a historic castle on the
north bank of the River Thames in central London, England.
Says Wikipedia, It was founded towards the end of 1066 as part of the
Norman Conquest of England. The White Tower, which gives the entire
castle its name, was built by William the Conqueror in 1078, and was a
resented symbol of oppression, inflicted upon London by the new ruling
elite.
The castle was used as a prison since at least 1100, although that was
not its primary purpose.
A grand palace early in its history, it served as a royal residence.
As a whole, the Tower is a complex of several buildings set within two
concentric rings of defensive walls and a moat.
The first bridge over the Thames was buikt by the Romans about AD 50,
or some 2000 years ago, says Wikipedia.
The King John version of the bridge completed in 1209. He licensed the
building of houses on the bridge, as a direct means of deriving
revenue for its maintenance, and it was soon colonised by shops.
The medieval bridge had 19 small arches and a drawbridge with a
defensive gatehouse at the southern end. Contemporary pictures show it
crowded with buildings of up to seven stories in height.
The buildings slowed down the traffic crossing the river. The houses
and shops took up space and could draw crowds, and when carts broke
down or animals misbehaved, crossing the bridge could take up to an
hour. For this reason, people on foot often chose to use the dozens of
river taxi boats that quickly ferried Londoners from shore to shore.
Nearly 200 places of business lined both sides of the narrow street.
Besides his six marriages, Henry VIII is known for his role in the
separation of the Church of England from the Roman Catholic Church,
says Wikipedia.
Henry's struggles with Rome led to the separation of the Church of
England from papal authority, the Dissolution of the Monasteries, and
establishing himself as the Supreme Head of the Church of England.
Henry was known by some to be an attractive and charismatic man in his
prime, educated and accomplished.[4] He was an author and a composer.
He ruled with absolute power.
His desire to provide England with a male heir—which stemmed partly
from personal vanity and partly because he believed a daughter would
be unable to consolidate the Tudor Dynasty and the fragile peace that
existed following the Wars of the Roses[5]—led to the two things that
Henry is remembered for: his wives, and the English Reformation that
made England a mostly Protestant nation. In later life he became
morbidly obese and his health suffered; his public image is frequently
depicted as one of a lustful, egotistical, harsh, and insecure
king.[6]
Tuesday, November 27, 2012
James Bond travels to cities once in the British Empire / Brandy Sells

James Bond travels to cities once in the British Empire / Brandy Sells, a photo by trudeau on Flickr.
20 cities round the globe: here's an example of completing the British Empire map review that is due next class.
Compliments to Brandy Sells.
1st semester exam Study Guide, world geography 2012-2013
Exam: 50 multiple-choice, open-notes questions taken from the questions on the class blog as seen below. Scored on Scantron forms.
Plus a brief comparison essay following the rubric on the class blog.
Poverty Point Quiz
1. The mounds at Poverty Point site are arranged in circular form around a central focal point. We call that a __ arrangement. concentric
2. The architectural sites built by ancient Indigenous peoples have been neglected by historians because they were built from __ . dirt
3. Monroe, Shreveport's latitudinal neighbor, lies upon the __ river. a) Ouachita b) Atachafalaya c) Pearl d) Sabine. a
4. The principal trail used by Caddo people connected the state of __ to Louisiana. tx
5. Every day two great gifts arrive in Louisiana from distant Montana. They are the resources a) coal and electricity b) coal and timber
c) coal and water d) coal and petroleum. c
6. Future conflicts between Louisiana and Texas may arise from claims of ownership in regards a key resource, __ . water
Indigenous people
1.The word for native people: a) indigent b) indigenous c) indeginous d) indingenous. b
2. The most northerly of the states associated with the Caddo. __ ok
3. Which is the most northerly of the Mississippi tributaries? __ Missouri
5. Which state lies between Minnesota and Missouri on the western edge of the Mississippi? __
Name the significant river associated with the following -
1. Minnesota - Ms
2. Montana - Mssouri
3. Pennsylvania - Ohio
4. Illinois - Ohio
5. Texas - Red
A slow-moving internet: the Mississippi River and tributaries
1. Name the 5 states that lie adjacent to and west of the Miss. Their initials are MIMAL.
2. Name the 5 states that lie east of the Miss. Initials: WIKTM.
3. The Mississippi R. is the second longest in the US. Even longer is the Missouri. Name 2 states associated with the Missouri.
Choose from Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Nebraska, Iowa, Kansas, Missouri.
4. The state in which the Mississippi begins its course: __. Minnesota.
5. The Miss. R. is connected to the Great lakes. T / F
It is not connected by the natural course of the Mississippi. A canal called the Illinois Waterway was created to make a man-made connection.
6. The longest tributary on the east is the Ohio R. Name 2 additional states through which it passes. Choose fromPennsylvania, Ohio, West Virginia, Kentucky, Indiana, Illinois.
7. Name the 5 Great Lakes of the US, giving their names as read from left to right. Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie Ontario.
8. Which tributary has its headwaters in Montana? Missouri R.
9. Which is more northerly, Memphis or St Louis? St Louis.
10. Which tributary begins in Texas? the Red River.
11. What is the significance of the Miss Valley? Recreation, waste disposal, water supply, fishing, grain export, petro-chemical exports and manufacturing exports are among the ways the Mississippi enriches the US.
12. Why is it like a slow-moving internet? Because it is a conduit for information, goods and services and profit.
The Robot quiz for non-robots
1. The high school-level social studies project is one that requires students to demonstrate competence in using the __ method. sci
2. Gathering evidence in the social studies project must be accomplished via quoting articles, books and at least one __ . interview
3. Which Arkansas mountain range is found the state's north? a) Ouachita b) Ozarks. b
4. Which Texas city is notable for digging a ship channel to make the city a port? The channel connects the inland city with a bay and thus connects to the Gulf of Mexico. Houston
__ .
5. In the NY Times story on robotics, the famous electronics giant, the Philips Corporation, is mentioned. Philips, inventor of the cassette tape (1962), is a company based in the nation of the __ . NL
6. "Video cameras guide them through feats well beyond the capability of the most dexterous human." "Dexterous" must mean a) having physical or mental agility b) high achievement in reading comprehension c) carefully trained. a
7. The NY Times story suggests that 10 robots ("about a tenth as many as the plant in the Chinese city of Zhuhai") can equal the labor of __ humans. a) 20 b) 50
c) 100 d) 1000. d
8. Name of the much-publicized Chinese manufacuring giant that makes iPhones, among many products: a) Foxconn b) Zuhai c) Flextronics. a
The Rivers are Roads quiz
1. River that forms the boundary between Texas and Mexico: __ __ . rio
2. The border between Texas and Oklahoma is mostly defined by one river: __ __ . red
3. Most of the border between Texas and Louisiana is defined by the __ River. sabine
4. Dallas, Shreveport, Monroe, Jackson, MS, and Los Angeles have something in common. a) longitude b) latitude c) humidity d) petroleum. b
5. The Vieux Carre means the "Old section" and, in Louisiana, refers to the __ __ . FQ
6. The city of New Orleans developed in a __ bend in the river, thus giving the city one of its nicknames, the __ City. (same answer, both blanks) crescent
7. In the Katrina story of 2005, the city's problem was mainly the a) soil b) canals c) Lake Pontchartrain d) levees. d
The last question will be scored as a mini-essay for 3 pts. 8. Might a definition of the term "Arklatex" include Dallas-Ft Worth? In a two-sentence answer, use the term "latitude" and "proximity."
A visit to Mars
1. Number of miles traveled between earth and Mars: 104 __ a) thousand b) million c) billion d) quadrillion.
2. The speed of the spacecraft before entering the landing phase: ___ miles per hour.
3. The Mars rover represents some __ years of work.
4. A Martian year is almost equivalent to two Earthly years. T / F
5. Scientists believe that Mars once fostered tiny living organisms called microbes. T / F
6. The rover landed in Gale __ . a) plain b) crater c) river d) storm.
7. The inquiry is looking for evidence of __ .
8. The direction in which the rover will be driven will be determined by scientists' examinations of the __ shots.
9. A galactic forensic lab is part of the rover's deck. T / F
10. The million-watt laser will primarily destroy the lunar roaches that have obstructed refueling in past missions. T / F
11. The chemical composition of Martian rocks will be analyzed by observing the light emanating from them. T / F
12. The rover has a power generator whose fuel is __ .
Sailing the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico
1. Leaving Miami in 24 foot sloop, should the sails be set for Bermuda or the Bahamas?
2. Should the sloop head for Freeport or Nassau?
3. In what state is there a Nassau in the US?
4. Based on the map key, about how many miles are spanned by the Bahama islands?
5. About how many miles are there between the southern tip of the US and Cuba?
6. The next stop in this sail voyage might be the capital of Cuba: __ .
7. After taking on supplies, the rudder is set for the American tourist town famous for the gatherings seen each day to toast the sunset: __ __ .
8. Sailing north to Miami, the boat will be aided by the natural force of the __ __ .
9. Actually, landing the boat in a Cuban port is against US law. Because the US is struggling against the communist government in Cuba, we do not allow trade with the island nation. Such a prohibition against trade is called an __ .
10. Sailing parallel to the Florida Keys the boat is running close to the __ National Park.
Gulf Stream Quiz
Gulf Stream quiz
1. Columbus was not the first European to voyage to the New World. T / F
2. The capital of the Bahamas: __ .
3. Atlantic islands about 600 miles east of the South Carolina / Georgia border: __ .
4. Caribbean sea snail: __ .
5. Word for a sailboat race: __ .
6. Linking a tale about impoverished island kids with BB guns to the Caribbean is part of a learning or memory strategy called a __ .
7. In Jamaica people mostly speak English or a patois. In the Dominican Republic the language is Spanish. In Haiti the dominant language is __ .
Hispaniola quiz 9.12-13.12
1. Name the nation that lies between Cuba and the Dominican Republic. __
2. Which island is the largest US Territory in the Caribbean? __ __
3. Which is the only consecutively-doubled letter in the name of the great sea bounded by the Greater Antilles, the Lesser Antilles and the coasts of Central and South America? __
4. This nation lies south of Cuba and west of Haiti: __ .
5. This island nation is adjacent to the coast of Venezuela: __ .
6. This Kenyan city lies at 1S, 36E: __ .
7. The capital of Indonesia is the center of a megalopolis of some 26 million people. It is Jakarta. Write its coordinates.
Jerk chicken review
1. Name a Caribbean island on which English is a principal language.
2. Name an island on which French is a principal language.
3. Name an island on which Spanish is a principal language.
4. Name an island on which Dutch is a principal language.
5. Hispaniola is an __ .
6. The Cayman islands were named for a creature that is more or less an __.
NYC review
1. Name the island that has 2 boroughs.
2. Name the 5 boroughs of NYC.
3. Name the most densely-populated borough, which is the central island.
4. Name the southerly island borough.
5. Name the river on the west side of NYC.
6. Name the ocean adjacent to NYC.
7. Name the 2 states that are closest to NYC.
8. Name the 3 islands that surround New York harbor.
9. Name the 2 famous small islands in NY harbor. One has a museum of US Immigration, one bears a giant statue.
10. The body of water that separates Long Is and Connecticut has an archaic name: Long Island Sound (bay).
The Golden State quiz
1. Along the Pacific coast, Oregon through California, find the mountains called Coast Range. They are __ to the Sierra Nevada range. a) parallel to b) perpendicular to c) pretty close, but not what you would call too close.
2. Because the Coast Range mountains are low in height and very, very close to the Pacific shore, we can say they represent an example of a) subduction b) faulting c) spreading d) accretion.
3. The Sierra Nevada Range would be an example of a) subduction b) faulting c) spreading d) accretion.
4. The ___ National Park is immediately east of San Francisco. a) Yellowstone b) Navajo c) Yosemite d) Grand Canyon.
5. North of Los Angeles is the __ National Park. It is named for the giant redwood trees of California.
6. The name of the Mexican peninsula that lies to the south of California: __ California.
7. The map coordinates for Los Angeles.
8. Close to San Francisco you will find Palo Alto, the home of Stanford University, one of the world's top academic institutions. There is a business-oriented regional name that can be applied to the area around San Jose and Palo Alto. It is referred to as __ __ .
9. The San Andreas Fault extends well north of San Francisco. T / F
1a2d3a4c5Sequoia6Baja734N,118W8SiliconValley9T
Canada: It's a quiz, eh!
T 1. Canada’s population is about one tenth of the US population, although it is slightly larger than the US in area. T / F
A 2. An island in Eastern Canada came under British rule with the Treaty of Utrecht (1713). This resulted in a serious change in the population of a) Nova Scotia b) Quebec c) Massachusetts
d) Montreal.
B 3. Canadians often speak 2 languages, owing to their nation’s ethnicity: a) English & German b) English & French c) English & Inuit d) English & Canadianne.
B 4. Born and raised in Montreal: a) Michael Cera
b) Sieur d’Iberville c) Beausoleil d) Celine Dion.
A 5. The French who were born in Louisiana colony were called a) Creoles b) Acadiennes c) Cajuns d) Gumbo.
D 6. Between their impoverished life in Western France and their impoverished life as pioneers in Louisiana, the French colonists spent about 150 years in a) the Caribbean b) British Columbia c) Toronto d) Acadia.
B 7. Guy Laliberté and Daniel Gauthier founded a) Canadian Waste Disposals Systems b) Cirque de Soleil c) the rock band Rush d) Quebec City.
C 8. The nation’s capital: a) Quebec b) Montreal c) Ottowa
d) Toronto.
D 9. The Great Lakes connect to the Atlantic via the
a) Illinois-Michigan Canal b) Erie Canal c) Niagra Falls
d) St Lawrence River.
T 10. Part of Canada is an archipelago. T / F
B 11. “Canada is also geologically active, having many earthquakes and potentially active volcanoes,” says Wikipedia. This would refer to __ Canada. a) Eastern b) Western c) Northern d) Southern
D 12. The coordinates are 45N, 73W: a) Toronto b) Winnipeg c) Detroit d) Montreal.
B 13. Land area: which is larger, the a) US or b) Canada?
Geology quiz
1. The Appalachian range is an example of a) subduction b) faulting c) accretion d) spreading.
2. Geologists report in National Geographic magazine that the distance between North America and Europe is increasing each year by about 2.2 inches. That is an example of a) subduction b) faulting c) accretion d) spreading.
3. The Coast Range runs along the Pacific coast in California. They are small but craggy mountains. They are so close to the ocean shore that they seem to rise magically from the surf. They would be an example of a) subduction b) faulting c) accretion d) spreading.
4. The San Andreas Fault is a crack in the earth's plates that threatens the California rim with a devastating earthquake. It is an example of (be careful!): a) subduction b) faulting c) accretion d) spreading.
5. Write the coordinates for San Francisco. __ N, __ W.
6. Name the exciting Canadian city on the Pacific coast. Known for its fabulous aqaurium, vibrant Asian population and high-tech achievements, it is a city similar in size to Denver.
It is __ .
7. One of Facebook's chief officers is a woman known for encouraging females to enter the world of Silicon Valley-type businesses. She is Sheryl __ .
Tampico and Popocatepetl: Mexico
1. The US states that border Mexico: California, Arizona, __ __ and Texas.
2. The Yucatan Peninsula is closest to a) Texas b) Cuba c) Florida d) Jamaica.
3. Mexico has a Pacific coast and a Gulf of Mexico coast. Regrettably, it lacks a Caribbean coast. T / F
4. West and slightly north of the capital is the second largest Mexican city: ___ .
5. Mexico is part of Central America, a region called __ ("middle America") by archaeologists and historians.
6. The takeover of Mexico by Spanish conquistadors was made easier by the decimation of the population via ___ .
7. People from Europe discovered new food plants in Central America. One was the tomato. T / F
8. One of the plants discovered by Europeans was a powerful spice that also had medicinal effects. It was the __ __ .
9. This starchy plant was developed in the Andes Mountains of Peru and Ecuador. It was the a) potato b) avocado c) cacao bean d) peanut.
10. Trumpets, fiddles, guitars and harmonized vocals are typical of the Mexican folk music called __ .
From Tijuana to Sao Paulo
1. Ethnocentric terms include Old World and Middle East. T / F
2. Peanuts, pecans and potatoes were indigenous to Mesoamerica. T / F
3. The bean known as __ traveled from the Arabian peninsula to Europe to Mesoamerica.
4. Sugarcane was a crop indigenous to __ . a) Mesoamerica b) Asia c) Africa d) Europe.
5. Indigenous peoples in the Americas were decimated by disease following incursion by the a) slavers b) Africans c) aliens d) Europeans.
6. The Aztecs built cities and giant pyramids at Teotihuacan and Chichen Itza in central Mexico. T / F
7. The Aztec and Maya religious duty of __ __ was abhorrent to the Spanish.
8. The victorious leader of the Spanish conquistadores in the war with the Aztec was __ . a) Montezuma b) Cortez c) Avocado d) Zocalo.
9. It is a historic object of 24 tons that demonstrates high achievement in geometry and physics; it is the __ developed by Aztec astronomers.
10. Population growth by __ Americans represented the highest rate of ethnic increase.
11. US population: 72% __ . a) White b) African-American c) Latino d) Asian.
12. US population: 13% __ . a) White b) African-American c) Latino d) Asian.
13. US population total is approximately __ million.
14. The largest Brazilian cities are a) Sao Paulo and b) Rio de Janeiro. The metropolitan population of __ is about 11 million as opposed to the 6 million of the other city.
15. The national language of Brasil is not Spanish or English; it is __ . Must be spelled correctly.
16. Brasil's culture is famous for a nation-wide focus on futbol and __ . a) capoeira b) samba c) drumming, or percussion d) manufacturing.
17. Above is an instrument composed of string and stick, rock, gourd, shaker and stickette.
It is used to accompany the African martial arts-based dance called a) capoeira b) samba c) quilombo d) berimbau.
Squawk! Caw! Coates Bluff Trail review -
1. Tree whose bark has small growths that resemble tiny volcanic peaks: __ .
a) Cottonwood b) Hackberry c) Sycamore d) Dogwood.
2. This tree has a mottled bark and gargantuan leaves: __ . a) Cottonwood b) Hackberry c) Sycamore d) Dogwood.
3. Type of oak that is most prevalent in North Louisiana river bottoms: __ oak.
a) Live b) Water c) Pine d) River.
4. This tree produces "knees," a sort of knobby growth that pokes up through the ground in the vicinity of the tree. __ . a) Cottonwood b) Hackberry c) Sycamore
d) Cypress.
5. Tree that produces puce-colored blossoms (purplish-reddish-brown) in the late winter: __ __ . a) Cottonwood b) Redbud c) Sycamore d) Dogwood.
6. If this woods vine isn't the 5-leafed Virginia Creeper it must be __ . a) Cottonwood b) Redbud c) Sycamore d) Poison Ivy.
7. The principal forest grapes of North Louisiana: __ . a) Cottonwood b) Redbud c) Muscadine d) Virginia Creeper.
8. When clay, sand and silt occur in a mixed soil, it is called __ . a) riparian
b) loam c) topsoil d) alluvial.
9. Louisiana is widely-known as a state with unusually rich bird life. T / F
10. The zone along a bayou is __ land. a) riparian b) conservation c) aquifer
d) up.
11. A woody, thick vine: a) pine b) rattan
c) oak d) cypress.
12. Tree used in bioengineering, medicine and for objects made of the soft wood: a) cypress b) willow c) cottonwood d) pecan.
13. Canopy trees - the tallest - of the Coates Bluff area include cottonwood and __ .
Bayou Pierre Fauna
1. Riverine tree that is one of the tallest and largest American hardwoods: __ . a) Cottonwood b) Hackberry c) Sycamore d) Dogwood.
2. Tall tree with wide, indented leaves and whose bark peels: __ .
a) Cottonwood b) Hackberry c) Sycamore d) Dogwood.
3. Fast-growing, tall bottomland oak that is very important to wildlife in North Louisiana: __ oak .
a) Live b) Water c) Pine d) River.
4. This tree has a long history, a medicinal bark and roots are so widespread it is important in bioengineering.
a) Cottonwood b) Hackberry c) Sycamore d) Willow.
5. This tree produces woody projections that rise above the water or the ground in the vicinity of the tree. __ . a) Cottonwood b) Hackberry c) Sycamore d) Cypress.
6. Wine, jelly and a tart pie filling can be made from the __ grape of North Louisiana. a) Rattan b) Redbud c) Muscadine d) Virginia Creeper.
7. If this hairy vine isn't the three-leafed Poison Ivy it must be the __ . a) Rattan b) Redbud c) Virginia Creeper d) Sycamore.
8. Louisiana is known as a state with a rich bird life because the state lies in the flyway between Canada and the sea known as the __ _ __ .
9. The type of dirt called loam occurs when ____ , sand and silt occur in a mixed soil.
10. Riparian land is the zone along a ___ . a) waterway b) aquifer c) conservation region d) region of ripening fruits.
11. Acetylsalicylic acid: a) Cypress b) Willow c) Sycamore d) Pecan.
12. The highest-reaching trees of the Coates Bluff area include Sycamore and Cottonwood. They are called
__ trees. a) medicinal b) loam c) riverine d) canopy.
13. Which one of these does not typically grow in the riparian zone? a) Water oak b) Willow c) Hickory d) Hackberry.
14. This widespread tree is helpful for many but considered a noxious invader by those who want to avoid a monoculture and insure biodiversity. It is the Chinese __ .
a) Candle b) Fruit c) Tallow d) Redbud.
Use this list of cities and nations in answering questions on what was once the British Empire.
1. London
2. Dublin
3. Gibraltar
4. Lagos, Nigeria
5. Cape Town, South Africa
6. Nairobi, Kenya
7. Mocha, Yemen
8. Jerusalem, Palestine (today, Israel)
9. Baghdad, Iraq
10. Mumbai (Bombay), India
11. Delhi, India
12. Kolkata (Calcutta), India
13. Singapore, formerly Malaysia
14. Hong Kong, China
15. Sydney, Australia
16. Port of Spain, Trinidad
17. Kingston, Jamaica
18. NYC
19. Toronto, Canada
20. St George's, Bermuda
Monday, November 26, 2012
The many cultural connections to the British Empire
Gold and gemstones were underlying reasons for many of the territories added by the Brits to their vast empire.
Building an empire was not about the Church of England or democracy or giving technological advancement to the primitive peoples. It was aimed at building British wealth.
What goes up, alas, must come down. In the late 20th century the English colonies demanded their independence. Having lost most of their colonies, the British have carried on as a normal, post-colonial nation.
Recent decades have seen Britain losing its strength in manufacturing and technological innovation. Their economy is down.
The good news is that English remains a powerhouse in entertainment. Examples are Adele, the James Bond movies, British comedies and dramas and fashion. They remain effective at marketing, pharmaceuticals and building aeroplanes. And they have oil reserves in the North Sea.
Sunday, November 25, 2012
Mapping a global adventure undertaken by MI6 Agent 007, James Bond
Sketch the outline of a world map over a 2-page spread.
Identify city and nation - in color - and bodies of water in James Bond's journey across cities that were once owned by the British.
1. London
2. Dublin
3. Gibraltar
4. Lagos, Nigeria
5. Cape Town, South Africa
6. Nairobi, Kenya
7. Mocha, Yemen
8. Jerusalem, Palestine (today, Israel)
9. Baghdad, Iraq
10. Mumbai (Bombay), India
11. Delhi, India
12. Kolkata (Calcutta), India
13. Singapore, formerly Malaysia
14. Hong Kong, China
15. Sydney, Australia
16. Port of Spain, Trinidad
17. Kingston, Jamaica
18. NYC
19. Toronto, Canada
20. St George's, Bermuda
- Five multiple-choice questions on the locations or resources of these colonies.And please add a colored Union Jack.
- Title, neatness, completeness: 15 pts.
English warships, soldiers and commanders built the British Empire, which grew in the 1600's and peaked in the early 1900's

Details of British warships by Willem Van de Velde the Younger and John Christian Schetky (4), a photo by mharrsch on Flickr.
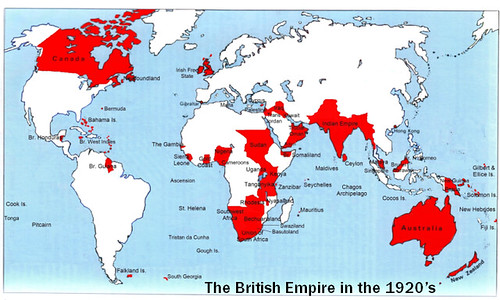
At its height, the British Empire was the largest empire in history and, for over a century, was the foremost global power, says Wikipedia.[1]
By 1922 the British Empire held sway over one-fifth of the world's population.[2] The empire covered almost a quarter of the Earth's total land area.[3][4] As a result, its political, legal, linguistic and cultural legacy is widespread.
At the peak of its power it was often said that "the sun never sets on the British Empire" because its span across the globe ensured that the sun was always shining on at least one of its numerous territories.
During the Age of Discovery in the 15th and 16th centuries, Portugal and Spain pioneered European exploration of the globe, and in the process established large overseas empires. Envious of the great wealth these empires generated, England, France and the Netherlands began to establish colonies and trade networks of their own in the Americas and Asia.[5]
The British Empire began to take shape during the early 17th century, with the English settlement of North America and the smaller islands of the Caribbean, and the establishment of private companies, most notably the English East India Company, to administer colonies and overseas trade.
Settlements were successfully established in St. Kitts (1624), Barbados (1627) and Nevis (1628).[25] The colonies soon adopted the system of sugar plantations successfully used by the Portuguese in Brazil, which depended onslave labour, and—at first—Dutch ships, to sell the slaves and buy the sugar.[26] The increasingly healthy profits of this trade were soon restricted to English ships.
From the outset, slavery was the basis of the British Empire in the West Indies. Until the abolition of the slave trade in 1807, Britain was responsible for the transportation of 3.5 million African slaves to the Americas, a third of all slaves transported across the Atlantic.[37] To facilitate this trade, forts were established on the coast of West Africa, such as James Island, Accra and Bunce Island. In the British Caribbean, the percentage of the population of African descent rose from 25 percent in 1650 to around 80 percent in 1780, and in the 13 Colonies from 10 percent to 40 percent over the same period (the majority in the southern colonies).[38]
For the slave traders, the trade was extremely profitable, and became a major economic mainstay for such western British cities as Bristol and Liverpool, which formed the third corner of the so-called triangular trade with Africa and the Americas. For the transported, harsh and unhygienic conditions on the slaving ships and poor diets meant that the average mortality rate during the middle passage was one in seven.[39]
The Battle of Plassey, 1757, saw the British defeat the Nawab of Bengal and his French allies, leaving the Company as the major military and political power in India.[51] In the following decades it gradually increased the size of the territories under its control, either ruling directly or via local rulers under the threat of force. British India eventually grew into the empire's most valuable possession, "the Jewel in the Crown"; covering a territory greater than that of the Roman Empire, it was the most important source of Britain's strength, defining its status as the world's greatest power.[53]
Since 1718, transportation to the American colonies had been a penalty for various criminal offences in Britain, with approximately one thousand convicts transported per year across the Atlantic.[64] Forced to find an alternative location after the loss of the 13 Colonies in 1783, the British government turned to the newly discovered lands of Australia. The Australian colonies became profitable exporters of wool and gold,[70] mainly due to gold rushes in the colony of Victoria.
Under increasing pressure from the British abolitionist movement, the British government enacted the Slave Trade Act in 1807 which abolished the slave trade in the empire.
Following the defeat of Napoleonic France in 1815, Britain enjoyed a century of almost unchallenged dominance, and expanded its imperial holdings across the globe. Increasing degrees of autonomy were granted to its white settler colonies, some of which were reclassified as dominions.
WWI placed enormous financial and population strain on Britain, and although the empire achieved its largest territorial extent immediately after the war, it was no longer a peerless industrial or military power.
After the end of the Second World War, as part of a larger decolonisation movement by European powers, Britain granted independence to most of the territories of the British Empire. This process ended with the political transfer of Hong Kong to China in 1997.
Semester exam: 50 questions plus a brief comparison essay
Semester exams span Dec 18 to 21.
Geography class exam comprises -
a) 50 multiple-choice questions taken from quizzes posted on the class blog. An open-notes test, some of the questions will have been tweaked to add an element of rigor to this test of reading comprehension.
Answered and scored on Scantron forms.
b) Brief comparison essay of any two not-ordinarily-relatable topics. Examples:
- Rolls Royce and Lake Michigan.
- Chief Tarshar and the Empire State Bldg.
- Venice, California, and the Gulf Stream.
If you have a comparison essay question, ask my approval during class - write it in your notebook and I will initial it - or via email.
The rubric (required elements) that will guide essay writing:
1. Colorful opening. There are 3 recommended ways to create an interest-getting opening: a) use a quote b) ask a question c) write with vivid description.
2. Blend the topics continually in the paper. Do not write a block of material about one topic and then write a separate block about the other topic. Integrate the topics as you offer insight and evidence.
3) Use comparison terms:
* different from,
* the same,
* both,
* similar to,
* Neither, ... nor,
* like X is (adjective),
* ... than X is (adverb) than.
* both, ...
* either...or
* likewise
* similarly
* although,
* but neither...
* nor
* however
* on the other hand
4. Specific examples must be used to support generalities. An example: generality - The Incredibles was an awesome movie. specific - The Incredibles appealed to me because the characters (especially the mom and the teen sister) were believeable. They sounded like people I know.
5. Grammar counts.
6. Spelling, too. When in doubt, see a dictionary or ask me.
7. Punctuation is paramount. Again, ask me or your Grammar Check software.
8. Include documentation via "according to ...". This means include your source - from World Book to your little brother - in the body of your writing. Usually you place it at the end of the first or second sentence, says Grammar For Today.
9. Write a snappy title. Ways to make a title fun are to tweak a song or movie title or use alliteration. Also, write an explanatory subtitle. Example: "Dinkas are Incredibles;" "Many refugees from the Sudanese Dinka tribe have moved from poverty in east Africa to comfort in the US."
Finally, please don't put quotation marks around your title - unless you are quoting someone.
Traveling the globe with James Bond: the Skyfall quiz
Morgan, Purvis, Wade and Logan: the Skyfall quiz
1. The Bond movie opens in an ancient city located at the edge of two continents, Europe and Asia. The city: a) Jerusalem b) Cairo c) Istanbul d) Athens.
2. The James Bond series, from novels to the movies and actors, is a product of people based in __. a) England b) USA c) Ireland d) Canada.
3. The Bond movies began in the 1960's with "Dr. No," which was released __ years ago. a) 20 b) 30 c) 40 d) 50.
4. The quest in Skyfall is for a list of undercover agents working for the Western, democratic nations. Their organization is __ . a) G20 b) NATO c) WTO d) GDP.
5. Eve Moneypenny is played by the British actress a) Thandie Newton b) Naomi Campbell c) Naomie Harris d) Carmen Ejogo.
6. "M" is the title given the person commanding the British intelligence command, aka __ . a) MIA b) MI6 c) MDA d) Z.
7. In Skyfall, the principal role of M is played by a) John Huston b) Edward Fox c) Queen Elizabeth d) Judi Dench.
8. Fighting the assassin Patrice, Bond sustains a wound that will provide an important clue in later action. He was assaulted by a __ . a) knife b) gun
c) hypodermic needle d) cyanide capsule.
9. Bond follows Patrice to a port city filled with futuristic office towers and hotels: __ . a) Hong Kong b) Macau c) Beijing d) Shanghai.
10. In the assassin's glass-cutting kit Bond finds a gold and red disc imprinted with a dragon and Chinese lettering. Viewers learn that the disc is a __ .
a) king's coin b) sign of the Chinese mafia c) gambling chip d) computer chip.
11. What essential role was played by the men above: Morgan, Purvis, Wade and Logan? a) writers b) directors c) designers d) producers.
More to come.
Answers found in the top-secret source called "W," or Wikipedia.
Monday, November 19, 2012
Thursday, November 15, 2012
Student essay: Dew-coated shoes on the Coates Bluff Trail
Dew-coated shoes on the Coates Bluff Trail
Journeying into the trail began with crisp crunches of dew-coated shoes on ample Sycamore and Cottonwood leaves. The surface of Bayou Pierre glistened at daybreak with a veil of wet mist blanketing the water; the air coming out of students’ mouths resembled the mist on the slow moving creek. The Coates Bluff Trail was encompassed with a cheerful hum of voices synchronizing with the chirps of birds, the trickling of Bayou Pierre, and the falling of tree limbs. About halfway through, there was a large decomposing tree, a safe haven for the indigenous bugs, preparing to morph into fertile soil as the wood splintered into soft moist wood. Red Chinese Tallow leaves dotted the ground as the class made their way to Montessori School of Shreveport. Students eventually walked back on the loamy path of tree roots.
The Coates Bluff Nature Trail is an important resource to the environment. Trees like the willow have acetylsalicylic acid, and are used for the common OVC drug Aspirin. Native Americans would even chew the bark to feel relieve to aches and pains.While the Chinese Tallow is know for its invasive monoculture in eastern Texas, it is crucial for honey foraging. Beekeepers will place their hives in the Tallow trees in the spring because of their nectarous blossoms for the bees. Fauna like armadillos are used to help scientists with the study of leprosy, and flora like the pine are used commercially for timber. The flora and fauna all combine together to keep a balanced web; the acorns of the live oak feed hungry animals. Canopy trees like the Sycamore and Cottonwood provide shade on hot days, and the cooling waters of Bayou Pierre, adjacent to Coates Bluff, provide a soothing climate. While vines are annoying, the Muscadine vine provides tart jams and pies. The trail benefits humans also to help them exercise, and learn to appreciate the value of a nearby recreational walk.
Isabella Van Savage
Wednesday, November 14, 2012
Geography / Merrie olde England
Rolls Royce, Land Rover, Jaguar, MG, Mini Cooper, Lotus, Aston Martin: England was once a nation of top engineering and manufacturing. Today most of those auto companies have closed or been bought by non-English companies.
The British economy has been in decline in recent years. There's no easy answer as to why they've slipped.
Notice the circular building in the lower screen above; it is the Globe Theater, home of Wm Shakespeare.
Also, see a sketch of the 17th-18th century London Bridge, the one with structures built on the bridge itself. While it made the passageway narrow, the buildings - retail shops - generated a steady tax revenue for the King.
A promontory called Lands End, UK
Land's End is a headland and small settlement in west Cornwall, England, within the United Kingdom. It is located on the Penwith peninsula approximately eight miles west-southwest of Penzance.
Land's End is the extreme westerly point on the mainland of England.
The climate in Cornwall is mild because the ocean has moderating influence on temperature.
The Isles of Scilly lie approximately 28 miles southwest - in the Atlantic.
The Gulf Stream flows past the Scillies and Cornwall as it flows to the North Atlantic.
Historic London pop-up map: 12 pts
- The Globe Theater, home to Shakespeare.
- The shop-crowded London Bridge of the 18th century.
- The Ancient castle called the Tower of London.
- The tower of Big Ben and the Houses of Parliament.
- The Thames River.
- The Roman name for the city: Londinium.
12 pts. Title, labeling, neatness.
Monday, November 12, 2012
The Basics of Rugby: part of an intro to Western Europe and the UK
"What may appear to be total chaos - is a game of rugby."
Selected items from the site http://www.rugby-sidestep-central.com/:
Players in the other team are allowed to tackle, hold, push or grasp the ball carrier but must not tackle or obstruct any other player.
None of your team are allowed to obstruct opposition players, including when they are attempting to to tackle your ball carrier.
Any player may kick the ball any distance in any direction.
Generally speaking team-mates should be behind the kicker when the ball is kicked or they will be "off-side" and may give away a penalty.
From time to time knots of players form spontaneously and become involved in contests for possession of the ball.
If the ball is on the ground it`s called a ruck and players must bind together and attempt to gain possession by pushing and stepping over the ball (rucking).
If the ball is off the ground it`s called a maul. Players must be bound together. They push and grapple , attempting to gain control of the ball (mauling) . A maul must keep moving or play will be stopped.
Even when a player breaks the rules play may continue if that is to the advantage of the opposing team. If there is no advantage a penalty kick is awarded for a serious offence or a scrum is set up for a minor offence.
A scrum is when the 8 forwards from each team pack down, head to head in one mass. The ball is put into the centre of the mass and the players attempt to win control with their feet and legs. No handling in the scrum!
Play also stops when the ball goes out of play over the touch-lines. It is restarted with a lineout where the ball is thrown in beteen the two lines of opposing players who leap to catch it.
Magnet geography: the UK
Learning the map of the UK via symbols
Magnet geography: the UK
Originally uploaded by trudeauSymbols may be effective learning tools, so allow me to suggest images that will connect with regions and the history of the UK.
- Northern Ireland: the HMS Titanic, which was built in the city of Belfast, N. Ireland.
- Ireland: The Guinness Book of World records - and a pint of black Guinness beer.
- Scotland: the green, cup, flag and driver used in a game of golf.
- England: the Rolls Royce, one of the great luxury cars.
- Wales: a British castle - built to control the rebellious Welsh forces.
- France: the helmet-wearing William of Normandy, aka Wm the Conqueror.
- Belgium: french fries; the Belgians and Dutch probably preceded the French in frying potato strips, says Wikipedia.
- Netherlands: a bicycle, because they are so widely used as daily transportation in Holland.
-Germany: the Volkswagen Beetle, a revolutionary little car created by Dr. Ferdinand Porsche at the request of German Chancellor Adolph Hitler.
- Roman Empire: a large building that suggests a Public Bathhouse.
Throughout the empire the Romans built baths as they did amphitheaters and fortresses.
- The Romans called England "Britannia." They called Ireland "Hibernia."
- Anglo-Saxons: for the Germanic tribes who were the first Celtic peoples of England I offer a giant oak tree, which was a typical spot for Druid-led worship of these pre-Christian peoples.
- Latin language: Roman numerals. Also, the quote from Julius Caesar: "Veni, vidi, vici." "I came, I saw, I conquered."
- Roman Catholic Church: a Gothic cathedral.
- William of Normandy: the Tower of London, built by him in 1066.
- British Empire: a globe, because the British controlled lands all across the world. It was said, "The sun never sets on the British Empire."
Riparian fauna: raccoons and opossums inhabit burrows as well as tree hollows
Tree hollows in old oaks or other trees and rock crevices are preferred by raccoons as sleeping, winter and litter dens, says Wikipedia. If such dens are unavailable or inconvenient, raccoons use burrows dug by other mammals, dense undergrowth or tree crotches.
Opossums are usually solitary and nomadic, staying in one area as long as food and water are easily available. Some families will group together in ready-made burrows or even under houses. Though they will temporarily occupy abandoned burrows, they do not dig their own. As nocturnal animals, they favor dark, secure areas. These areas may be below ground or above.
Raccoons are noted for their intelligence, with studies showing that they are able to remember the solution to tasks up to three years later. The diet of the omnivorous raccoon, which is usually nocturnal, consists of about 40% invertebrates, 33% plant foods, and 27% vertebrates.
Mississippi River Delta Marshes are morphing
From the Baton Rouge Morning Advocate
The mouth of the Mississippi River is moving north, and unless preparations are made in advance for those changes, the impact could be devastating, speakers at a recent coastal conference said.
However, the changes also present opportunities for navigation and coastal restoration, said Paul Kemp, vice president of the Louisiana Audubon Society’s Gulf Coast Initiative.
Waiting for the navigation system at the mouth of the river to “break” is not the way to handle the problem, especially when it’s known that it’s going to happen, Kemp said.
As with the levees in New Orleans, it’s clear that it’s more expensive to react to disaster than to prepare for it, he said during the “Answering Fundamental Questions about Mississippi River Delta Restoration” symposium Friday and Saturday at LSU.
“If you know that’s happening, you can actually get in front of it and take advantage of it,” Kemp said. “It’s not all bad.”
Knowing that the river is changing means there are opportunities to not only get more sediment into eroding coastal marshes, but to also make navigation channels in the river more stable in the future.
Sunday, November 11, 2012
Bayou Pierre fauna quiz
Bayou Pierre Fauna
1. Riverine tree that is one of the tallest and largest American hardwoods: __ . a) Cottonwood b) Hackberry c) Sycamore d) Dogwood.
2. Tall tree with wide, indented leaves and whose bark peels: __ .
a) Cottonwood b) Hackberry c) Sycamore d) Dogwood.
3. Fast-growing, tall bottomland oak that is very important to wildlife in North Louisiana: __ oak .
a) Live b) Water c) Pine d) River.
4. This tree has a long history, a medicinal bark and roots are so widespread it is important in bioengineering.
a) Cottonwood b) Hackberry c) Sycamore d) Willow.
5. This tree produces woody projections that rise above the water or the ground in the vicinity of the tree. __ . a) Cottonwood b) Hackberry c) Sycamore d) Cypress.
6. Wine, jelly and a tart pie filling can be made from the __ grape of North Louisiana. a) Rattan b) Redbud c) Muscadine d) Virginia Creeper.
7. If this hairy vine isn't the three-leafed Poison Ivy it must be the __ . a) Rattan b) Redbud c) Virginia Creeper d) Sycamore.
8. Louisiana is known as a state with a rich bird life because the state lies in the flyway between Canada and the sea known as the __ _ __ .
9. The type of dirt called loam occurs when ____ , sand and silt occur in a mixed soil.
10. Riparian land is the zone along a ___ . a) waterway b) aquifer c) conservation region d) region of ripening fruits.
11. Acetylsalicylic acid: a) Cypress b) Willow c) Sycamore d) Pecan.
12. The highest-reaching trees of the Coates Bluff area include Sycamore and Cottonwood. They are called
__ trees. a) medicinal b) loam c) riverine d) canopy.
13. Which one of these does not typically grow in the riparian zone? a) Water oak b) Willow c) Hickory d) Hackberry.
14. This widespread tree is helpful for many but considered a noxious invader by those who want to avoid a monoculture and insure biodiversity. It is the Chinese __ .
a) Candle b) Fruit c) Tallow d) Redbud.
Friday, November 09, 2012
Chinese tallow leaf in red: Bayou Pierre / Coates Bluff Trail, Shreveport
The Chinese tallow is considered an invasive, noxious species by those concerned with fields and large acreage.
It is considered a fast-growing, attractive shade tree by many homeowners.
Bees get pollen from tallow trees, says Wikipedia. And in Asia the tallow oil is harvested as a biofuel.
Thus we derive a hypothesis from this plant:
that many plants will have both useful and, at the same time, negative qualities.
Thursday, November 08, 2012
Willows, medicines and Coates Bluff Trail / geography
Say it slowly:
a ce tyl sa li cylic acid!
Aspirin.
From the bark of willow trees.
Coates Bluff Trail, Shreveport
Squawk! Caw! Coates Bluff Trail review -
1. Tree whose bark has small growths that resemble tiny volcanic peaks: __ .
a) Cottonwood b) Hackberry c) Sycamore d) Dogwood.
2. This tree has a mottled bark and gargantuan leaves: __ . a) Cottonwood b) Hackberry c) Sycamore d) Dogwood.
3. Type of oak that is most prevalent in North Louisiana river bottoms: __ oak.
a) Live b) Water c) Pine d) River.
4. This tree produces "knees," a sort of knobby growth that pokes up through the ground in the vicinity of the tree. __ . a) Cottonwood b) Hackberry c) Sycamore
d) Cypress.
5. Tree that produces puce-colored blossoms (purplish-reddish-brown) in the late winter: __ __ . a) Cottonwood b) Redbud c) Sycamore d) Dogwood.
6. If this woods vine isn't the 5-leafed Virginia Creeper it must be __ . a) Cottonwood b) Redbud c) Sycamore d) Poison Ivy.
7. The principal forest grapes of North Louisiana: __ . a) Cottonwood b) Redbud c) Muscadine d) Virginia Creeper.
8. When clay, sand and silt occur in a mixed soil, it is called __ . a) riparian
b) loam c) topsoil d) alluvial.
9. Louisiana is widely-known as a state with unusually rich bird life. T / F
10. The zone along a bayou is __ land. a) riparian b) conservation c) aquifer
d) up.
11. A woody, thick vine: a) pine b) rattan
c) oak d) cypress.
12. Tree used in bioengineering, medicine and for objects made of the soft wood: a) cypress b) willow c) cottonwood d) pecan.
13. Canopy trees - the tallest - of the Coates Bluff area include cottonwood and __ .
Essay on Coates Bluff Trail, Shreveport
Description! "Trees of every size - sycamores, cottonwoods, etc - surrounded the students as they trekked a half mile on Coates Bluff Trail, Shreveport."
Description: "Birds squawked high above the trees on Coates Bluff Trail. Soon they would be landing in the canopy trees, the sycamores and cottonwoods, to begin finding food in the Coates Bluff woods - not far from the Red River.
Make your first paragraph one of description.
Your second and final paragraph must explain the value of the Coates Bluff environment. Be specific as you look at the scientific and medical value of the flora and fauna, the value of a wilderness trek to humans and mundane uses of the flora and fauna.
12 pts.
Thursday, November 01, 2012
Magnet geography: Coates Bluff map
Coates Bluff / riparian flora and fauna (riparian refers to the bank of a stream)
__Sycamore: tall tree; peeling bark and large leaves.
__ Cottonwood: one of the largest N Amer hardwood trees. Riverine (usually grows in river bottoms).
__ Water oak: fast-growing, tall bottomland oak that is very important to wildlife.
__ Willow: medicinal bark, extensive root system, used in wood products industry.
__ Hackberry: medium-sized tree important to the lumber industry and to wildlife. The bark is studded with warts.
__ Dogwood: though a small tree, its leaves (ink, dyes) and wood (mallets, tool handles) have long been useful in small industry.
__ Box elder (a type of maple): medium-sized tree of the bottom land.
__ Virginia creeper: a ground cover that inhibits erosion. Medicinal plant - but the berries are poisonous. Similar to poison ivy but has 5 leaflets instead of 3.
__ Muscadine vine: wine or jam is made from tart muscadine grapes. Anti-cancer properties in the grapes.
__ Poison ivy: a noxious weed of which it is said, "Leaves of three, let it be," "Longer middle stem, stay away from them," and "Hairy vine, no friend of mine." It can grow as a shrub or a vine.
Upland growth
__ Hickory: important source of wildlife food; wood is useful in numerous industries (from lumber to smoked meat).
__ Live oak: an evergreen known for its long life and spreading branches; important to wildlife for its acorns and known for strength of its wood.
__ Pine: commercially important for timber and wood pulp. They are fast-growing softwoods that live in the uplands.
Fauna
__ Armadillos: burrowing mammals with a leathery shell that eat insects. Important to scientists.
__ Hawks or falcons: swift birds of prey.
__ Black snake: non-poisonous and hibernating in the winter. They eat rodents, eggs and other snakes.
Smells
__ Loamy (loam is soil composed of clay, silt and sand.) and sandy soil. Decomposing leaves.
Sounds
__ Crows. Hawks. Mockingbirds. Sparrows.
__ Critters escaping though the leaves.
Non-woodsy materials
__ Litter.
__ Fencing, gravestones, etc.




![Skyfall [James Bond] 023 by FromFranceDavid](http://farm9.staticflickr.com/8465/8142107408_923f532fc5.jpg)