Tai chi chuan is an internal Chinese martial art. Tai chi is typically practised for a variety of reasons: its soft martial techniques, demonstration competitions, health and longevity. Consequently, there exist a multitude of training forms, both traditional and modern, which correspond to those aims. Some of Tai chi chuan's training forms are well known to Westerners as the slow motion routines that groups of people practice together every morning in parks around the world, particularly in China.
The Mandarin term "tai chi chuan" literally translates as "supreme ultimate fist" or "boundless fist," but may better translate to "great extremes boxing," with an emphasis on finding balance between two great extremes. The concept of the "supreme ultimate" is the symbol of the Taijitu meant to show the principles of Yin and Yang duality of Taoist philosophy. Thus, tai chi theory and practice evolved in agreement with many of the principles of Chinese philosophy and Taoism in particular. Tai chi training first and foremost involves learning solo routines, known as forms (套路 taolu). While the image of tai chi chuan in popular culture is typified by exceedingly slow movement, many tai chi styles (including the three most popular, Yang, Wu and Chen) have secondary forms of a faster pace.
In Western countries Tai Chi Chuan is often known simply as "Tai Chi" (with a corresponding emphasis on health practise and a de-emphasis on martial art training).
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
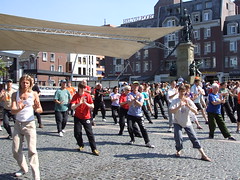

No comments:
Post a Comment